Density of state (DOS)
Introduction
- Density of States (DOS) represents the number of available electronic states at some energy.
- It is a fundamental concept in solid-state physics and materials science, providing crucial information about the electronic structure and properties of materials.
Physical meaning of DOS
Fundamental concept
- DOS represents the number of states available for electron occupation at energy .
- Higher DOS indicates more states available for electron occupation, which is often useful for electronic conduction, making/breaking chemical bonds, magnetization etc.
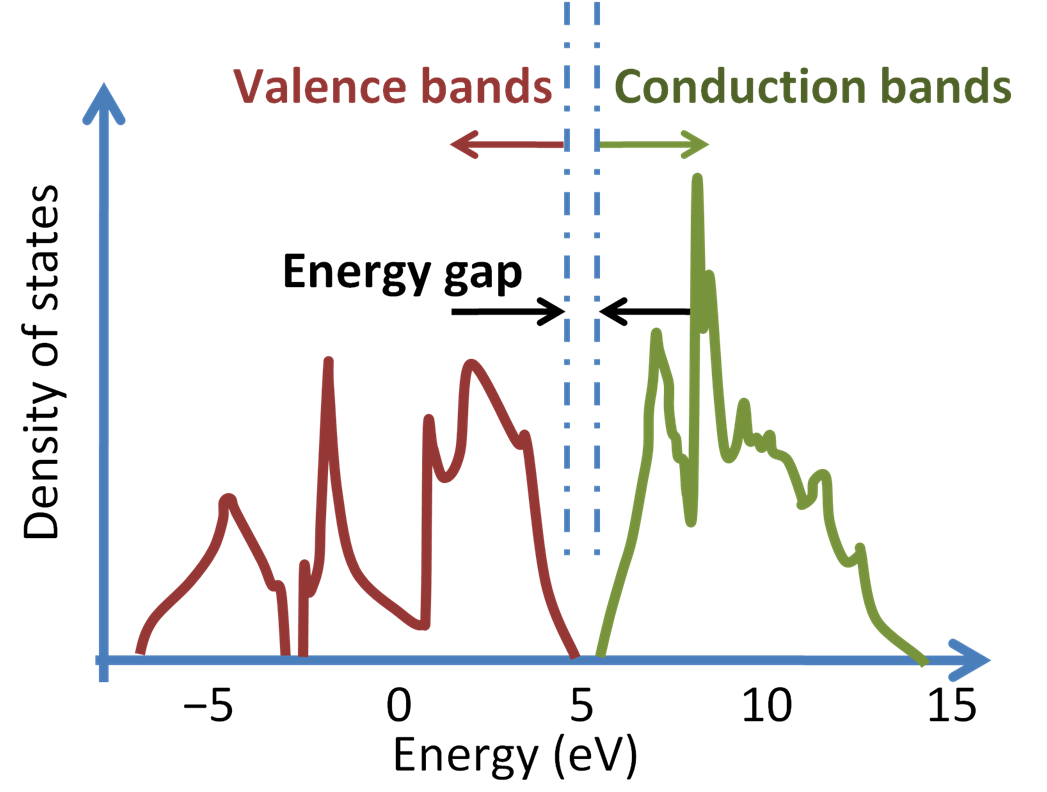
- The energy region with (1) non-zero DOS, (2) below the Fermi energy is called the valence band, and the region with (1) non-zero DOS, (2) above the Fermi energy is called the conduction band. The zero-DOS region between the valence and conduction bands are called the band gap.
Mathematical Definition
- Formal definition:
where:
- : the energy eigenvalues
- runs over bands
- runs over k-points in the Brillouin zone
- is the Dirac delta function
- In practice, function is replaced by a finite energy range (), so the DOS means the number of electronic state within this energy gap.
Integration Properties
- Number of electrons:
- Total energy:
- is the Fermi energy.
Practical DOS Calculations
Detailed Calculation Steps
- Usually, the geometry optimization is done before the DOS calculation.
- If the
LDOStag is set to.TRUE., the DOS calculation is done at the last step of geometry optimization. So separate single-point calculation at the optimized geometry is usally not necessary. - If you want to do DOS calculation at higher k-point mesh or higher cutoff energy, you can take the separate calculation.
INCAR
- No specifical tag is necessary to output the total DOS, but
LORBITneed to be set when PDOS is needed (mentioned later). - Note that the correct DOS cannot be obtained unless the number of k-points is sufficiently large.
The smearing parameters in the
INCAR(ISMEAR, SIGMA) also affect the accuracy of the DOS.Structure Optimization:
IBRION = 2 # Ion relaxation NSW = 100 # Number of ionic stepsDOS Calculation:
IBRION = 0 NSW = 0 LDOS = .TRUE. # actually this is default
After VASP calculation
- A file called
DOSCARwill be output. - Be aware that the output differs between spin-polarized and non-polarized calculations.
- For non-polarized calculations, the meaning of each column in
DOSCARis as follows:energy DOS integrated-DOS
Making plottable DOS file
DOSCARhas many sections, so it is not easy to make plot from it.- It is useful to use
vaspkitfor this purpose.
Installing vaspkit
- Go to vaspkit website: https://vaspkit.com/index.html
- Go to the "latest release page" (in SourceForge).
- Find the latest tar.gz file for Linux, and get the URL.
- Go to your VASP-installed-computer (supercomputer).
- Download the tar.gz file by using
wget(wget URL). - Extract with
tar zxvf vaspkit-xxx.tar.gz. cd vaspkit.x.x.xsource setup.shsource ~/.bashrc
Using vaspkit
- vaspkit is quite easy to use. Just type
vaspkitin terminal, and follow the instruction. - Total DOS
- To generate the DOS-related functions, type
11. - To get the total DOS, type
111. - Total DOS file
TDOS.datis generated. The energy position is shifted so as the Fermi energy becomes 0.
- To generate the DOS-related functions, type
Plotting the DOS
- Copy
*.datfile generated from vaspkit. Now it is easy to make plot. - Any software (Excel, Gnuplot, etc) is OK.
- When using gnuplot, the command becomes like
gnuplot > plot "TDOS.dat" using 1:2 with lines > plot "TDOS.dat" using 1:2 with lines, "TDOS.dat" using 1:3 with lines # when spin-polarized case
Projected DOS (PDOS)
- The PDOS refers to the DOS decomposed by angular momentum (s, p, d, etc.).
- To get the PDOS, use
LORBITtag inINCAR.LORBIT = 10: makes s-, p-, d-decomposed DOSs.LORBIT = 11: makes s-, px-, py-, pz-, dxy- ... DOSs.
- Plotting procedure is same with the total DOS.
- If you want to take the information of the d-band (to calculate the d-band center, for example), you should use PDOS.
Localized DOS (LDOS)
- LDOS refers to the DOS calculated separately for each atom.
- LDOS can be obtained from
vaspkit. - If you want to focus on the oxygen atom 2p band (often denoted as band), both localization and projection is needed.